Mold in the Toilet

Mold in the Toilet
The bathroom is a room that’s very susceptible to mold growth, and once you understand what mold needs to grow, it’s easy to understand why. Basically, it just needs moisture (shower=check, sink=check, toilet=check), and food (dust=check, organic matter=check), so the bathroom sometimes becomes a petri dish that’s hard to keep up with. Fortunately for you, we’re tackling this problem by appliance, so check out our other articles here:
- Getting rid of the ICK: Mold in the Shower
- “Sink” those microbes
- How can bacteria possibly grow in/on my soap?
Now, back to mold in the toilet. Mold can be mistaken for those stubborn mineral toilet rings, until it starts to turn weird colors, like black, brown or pink.
What type of mold is the black mold in the toilet?
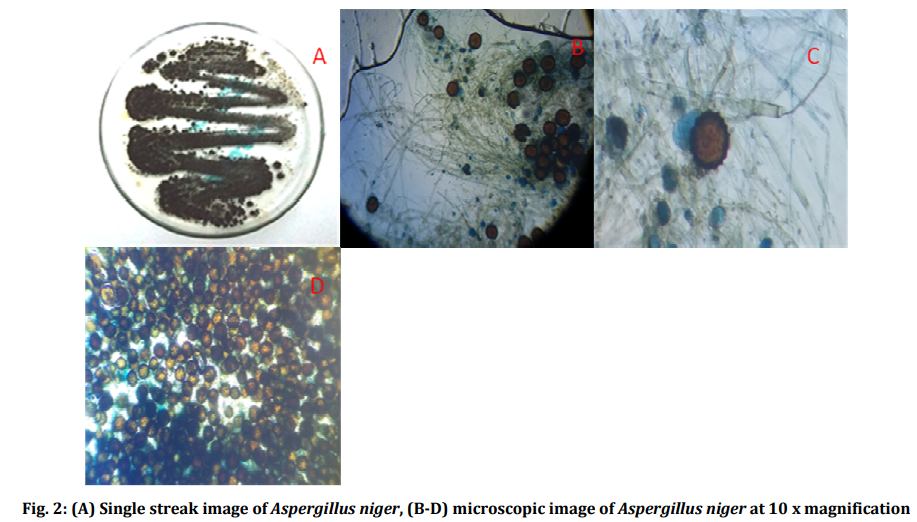
Although you may know that Stachybotrys chartarum is the most commonly termed “black” mold, another mold that appears black is Aspergillus Niger, as shown in Figure 2 of this 2017 study from India. Aspergillus Niger can be a cause of some forms of pneumonia, so it’s definitely not something you want in your bathroom! The study identified five types of mold in public toilets, resulting from airborne spread of spores and improper or infrequent cleaning procedures.
Alternaria and Cladosporium are two other types of mold that can produce black growths. (10 Types of Mold Colors Commonly Found in the House) The most important thing to know is that these molds can produce mycotoxins and mVOCs every time they are disturbed! Stachybotrys has been demonstrated to produce a number of Macrocyclic Trichothecene mycotoxins. (Black Mold and Stachybotrys Exposure Guide) Aspergillus niger can produce Ochratoxin A, Cladosporium produces mVOCs which can be irritating, and Alternaria species produce more than 70 mycotoxins! (Alternaria host-specific (HSTs) toxins: An overview of chemical characterization, target sites, regulation and their toxic effects)
Brown stains in the toilet are another problem–they could be caused by a number of molds, such as Pithomyces chartarum, Aureobasidium pullulans, Stemonitis, Taeoniella, Cladosporium or Mucor. Arguably the most harmful mold of these is Mucor, which can cause a life-threatening blood infection called mucormycosis. However, it’s not always brownt any point during its life cycle it can be brown, yellow, black, white, or gray. (10 Types of Mold Colors Commonly Found in the House)
Pink slime in the toilet is actually not mold. As we mentioned in our article about the shower, that pink slime that can also form around drains and at the bottom of the shower curtain is caused by the bacteria Serratia marcescens, and can cause urinary and respiratory tract infections, which are especially problematic for people with immune problems.
If you decide to try to find out what type of mold is growing, you can test it with a lab, but in any case it’s wise to treat it as a dangerous air pollutant. Don’t disturb it unless you spray a cleaner on it first (to immobilize the spores), or are using a mask!
What is the cause of mold in the toilet bowl?
There are several possible causes for mold in the toilet bowl, some of which can be easily resolved and some need more effort!
- One of the easiest methods is just flushing the toilet more often. Toilets that are not used every day can allow mold and bacteria to attach to the bowl. After cleaning the toilet, try to remind yourself to swing by and flush the toilet at least every other day so that these microbes don’t have a chance to proliferate.
- Next, if the toilet does get used or flushed often, more frequent cleaning is often needed. However, you need to skip traditional bleach based toilet cleaners, as they are toxic for you! The following are some non-toxic cleaners that are very effective for bacteria and germs, however note that citric acid is not always effective on mold (read below on citric acid** and get a few more recommendations from Zero-Waste Memoirs):
- Force of Nature is hypochlorous acid, a safe alternative to bleach that is a hospital-grade, EPA-registered disinfectant that kills 99.9% of germs including Staph, MRSA, Norovirus, Influenza A, Salmonella, and Listeria when used as directed. You can spray Force of Nature in the toilet as a final disinfectant, but it should not be mixed with essential oils or cleaners that contain essential oils, as this can reduce its disinfecting power.
- Fragrance-free powder: Seventh Generation Zero Plastic Toilet Bowl Cleaner ($22) has citric acid as its main cleaning agent. This non-toxic ingredient is registered with the FDA in products certified to kill feline calicivirus (a testing substitute for norovirus), so we know that it works. If you or anyone in your household is exhibiting symptoms of this illness or a similar one, we would suggest cleaning toilets full-strength and often with a product like this! If you like a little lemony fragrance, try the Probiotic Toilet Bowl Cleaner by Etee ($45), which also uses citric acid. It may seem expensive, but it’s not bad on a per-use basis ($1.50), and some customers find that using less than the prescribed amount (1 TBSP) works just fine. Added probiotics help to keep your septic system functioning optimally.
- Dissolving strips: Nature Clean Natural Toilet Bowl Cleaners Strips ($17) are highly rated too. They use sodium coco sulfate as the main ingredient, which is a blend of the fatty acids in coconut oil. (Sodium Coco Sulfate: Is It Natural?) It is a synthetic detergent with one of its ingredients being sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), however it is less irritating should you immerse your skin in the soapy water (highly unlikely for a toilet bowl cleaner!) Lastly, the essential oils including Australian tea tree oil, provide a pleasant scent and antiseptic properties.
- Liquid: Mrs. Meyer’s Liquid Toilet Bowl Cleaner, $6, uses citric acid and essential oils like lemon verbena to get a fresh-smelling clean, all in a bottle made from at least 30% post-consumer plastic (recycled).
Safe descaling of your toilet bowl: mineral stains and some molds may be removed by simply using the concentrated citric acid** (as you’ve read, a non-toxic ingredient in many toilet bowl cleaners), which comes in a granule or powder form. Granules are safer to use because they are mostly dust-free (they’ve been formed into little clumps that don’t kick up dust when you handle them).
The following is adapted from a post on Moral Fibres. Their method did not work without scrubbing but I learned a few things working on my own toilets:
Gather your supplies: a large pitcher for clean water, ½ cup of citric acid powder or granules, latex or plastic gloves, an abrasive scrub sponge that’s safe for porcelain, Bar-Keeper’s Friend Cleanser (optional), several paper towels, small disposable cup, tape for closing the lid (optional), about ¼ cup baking soda.
Turn off/close the water valve on the wall completely.
Flush the toilet. The tank and the bowl won’t refill this time.
Fill a large pitcher full of hot water from your sink and pour it into the toilet bowl. The water should not be boiling hot as it could crack your toilet. Also, make sure to add it slowly so that the water doesn’t drain completely from the bowl; you’ll want the water at or above the water ring stain.
Put on gloves and add about ½ cup of citric acid powder or granules to your toilet bowl. (use a mask if your citric acid comes in powder form)
Swish the water in the bowl gently with your toilet brush to dissolve it, but don’t swirl too vigorously because it will cause water to drain from the bowl. After you add the citric acid to the bowl, don’t add more water, because this will dilute the acid. Add paper towels around the bowl to cover all the stained porcelain, and use the disposable cup to wet them with liquid from the bowl. The bowl should be lined with paper towels stuck to the inside wherever there are stains.
Close the lid and put tape and a sign to prevent people from using it!
Leave the citric acid in the toilet bowl, without flushing, for at least one hour, or preferably before going to bed, so it can soak the scale overnight.
After leaving the solution to soak, use the bowl brush or gloved hands to remove the paper towels, and try using your toilet brush to remove scale deposits. If it doesn’t move, use gloved hands, the scrub sponge, and Bar-Keeper’s Friend or another agent safe for porcelain. Scrub away!
Finish by adding the baking soda to neutralize the acid, swish with the bowl brush, open the water valve, wait for the tank to fill, and flush!
If your toilet is particularly stained, then it may need a second application to remove stubborn deposits.
Citric acid**: The interesting thing about this chemical is that it is commercially produced by the mold Aspergillus Niger, which may be the same type of mold you’re trying to eliminate. Manufactured Citric Acid (MCA) is one of the most common food additives in the world, and has received the status of “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS) with the FDA. However, there have been isolated cases of inflammation due to ingestion of foods with MCA, due to its great tolerance to heat and large potential that byproducts of A. niger remain in the final MCA product. (Potential role of the common food additive manufactured citric acid in eliciting significant inflammatory reactions contributing to serious disease states: A series of four case reports) Unfortunately, we weren’t able to determine whether MCA actually kills Aspergillus Niger growing in your toilet, but it does a great job with all the other molds
The atmosphere of the bathroom is also very important in preventing mold. Here are two ways to keep the air in the bathroom less hospitable to mold:
- Bathroom exhaust fans are a must for any bathroom with an actual shower or bath. If you have a fan but not sure if it’s large enough, check the cubic feet of air per minute rating (cfm) on the fan (you may have to remove the cover) and this article to see if it’s large enough for your bathroom. In addition, go outside and see if you can see the little flapper lifting to show that air is indeed being exhausted. If you can't find the exhaust of this fan, it's possible that the moisture is being exhausted in the attic, which needs to be fixed. If your kids or guests are not switching on the exhaust fan during their showers, get an electrician to tie the fan and light switch together so that the fan MUST come on when the light is on. Finally, if you don't have an exhaust fan, get a window fan like this one and make sure the kids use it!
- Bipolar ionization units like our Germ Defenders, Mobile Air Angels and Whole Home Ionizers are a great way to keep mold away too. At the very least, plugging a Germ Defender into the bathroom will send out ions to kill mold spores in this small space where air circulation can be a challenge.
If the mold keeps coming back despite flushing and cleaning, then there are several possible causes for this:
- Older toilets commonly have pitting in the ceramic which can harbor mold. This video shows that no matter how hard a toilet is scrubbed with different products, pits in the ceramic are microscopic reservoirs that shelter bits of the mold, allowing it to come back again. The safest solution in this case is to replace the old toilet with a new one. The radical (but toxic) solution to keep your old toilet but lose the mold is to use diluted muriatic acid (also known as hydrochloric acid) to clean the pits. However, the mold will eventually come back and inhabit those pits again unless you take another step to renew the enamel on your toilet bowl (a bit extreme to save an old toilet).
- Improper venting. You may not know it, but all drains in your home require a vent to work properly. We’re not talking about the air vents in ceilings and walls, but a gas vent for the drain line. These are hidden in your walls. According to the uniform plumbing code, vents must be located within six feet of the P-trap (that snake-like part under the sink and the S-curve under the back of the toilet); otherwise, the drain may not work properly and gasses can build up, supporting mold and microbe growth. If this seems to be the case, it’s best to have a good plumber check out the location and condition of the toilet and sink vents and see if there are other drain problems.
- This next one is a difficult truth: there may be a cache of mold hidden in your home that is “seeding” spores into your air, causing mold to grow wherever there’s a water source (sinks, showers, and of course your toilet). According to a respected mold inspection and remediation company, Mold hotspots include the basement, attic, windowsills and door frames, crawlspaces, appliances, and underneath the sinks. Do you feel worse in some rooms of your home and better after leaving them? This gives a clue to where the mold contamination may be originating. If you don’t see anything obvious, you could have a hidden leak somewhere, like in the walls or flooring, that’s allowing mold to grow. There are two things you can do in this case:
- Order some spore traps from GotMold or even just a set of EC3 test plates ($36 for 6-pack) by MicroBalance Health Products to check the relative mold level in rooms to narrow it down!
- If you suspect a problem or are having chronic symptoms, it’s best to hire a qualified mold inspector.
There are many non-toxic ways to clean and keep clean nowadays, and with a little research and effort the toilet can be as clean and healthy as the rest of your bathroom and home!







